InceptionNet
1.GoogLeNet
The architecture of GoogLeNet is designed carefully to achieve the better utilization of computing resources by increasing the depth and the width of network while keeping the computational budget constant and the improved performance of model .
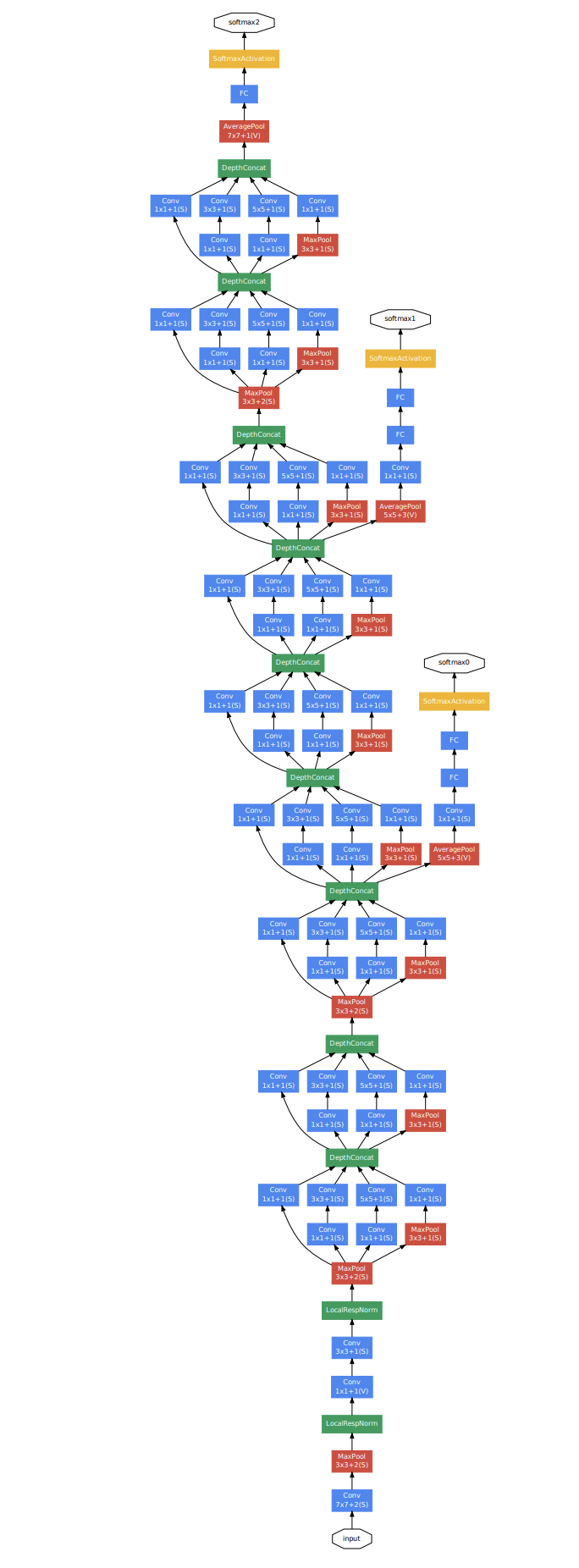
The most straightforward way of improving the performance of deep neural networks is by increasing their size including the depth and width, however, this will result in over-fitting due to the vanishing gradient resulting from the correspondingly dramatic increase of the network parameters. Another drawback of uniformly increased network size is the dramatically increased use of computational resources, an efficient distribution of computing resources is preferred to an indiscriminate increase of size.
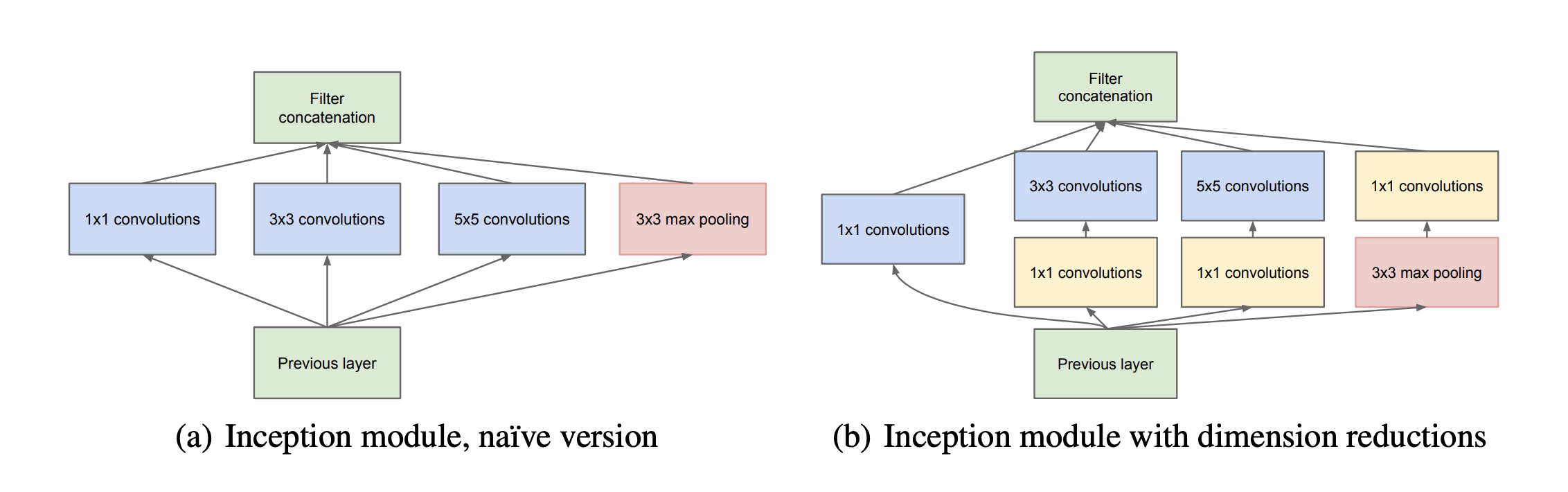
The main idea of the Inception architecture is based on finding out how an optimal local sparse structure in a convolutional vision network can be approximated and covered by readily available dense components. Besides, we apply the \( 1 \times 1\) convolution before \( 3 \times 3\) and \( 5 \times 5\) convolution to reduce the dimension of concatenated filter output.
The Inception module is as follows:
2.Inception-v2-v3
Training Deep Neural Networks is complicated by the fact that the distribution of each layer’s inputs changes during raining, as the parameters of the previous layers change. This slows down the training by requiring lower learning rates and careful parameter initialization, and makes it notoriously hard to train models with saturating non-linearity. Inception-v2 ensembles the Batch Normalization into the whole network as a regularizer to accelerate the training by reducing the Internal Covariate Shift. With the help of BN, the learning rate could be bigger than without it to reduce the training time.
The original Inception block is illustrated as following picture:
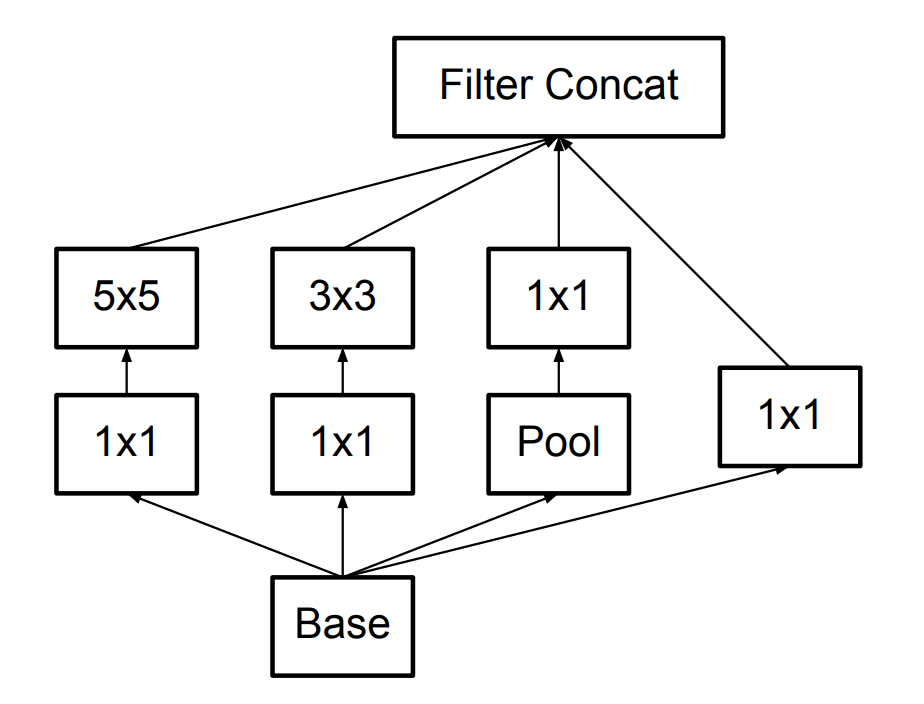
There are two important strategy to further reduce the computation cost:
- Factorization into smaller convolutions: Replacing the \( 5 \times 5 \) convolution with the two consecutive smaller \( 3 \times 3 \) convolution.
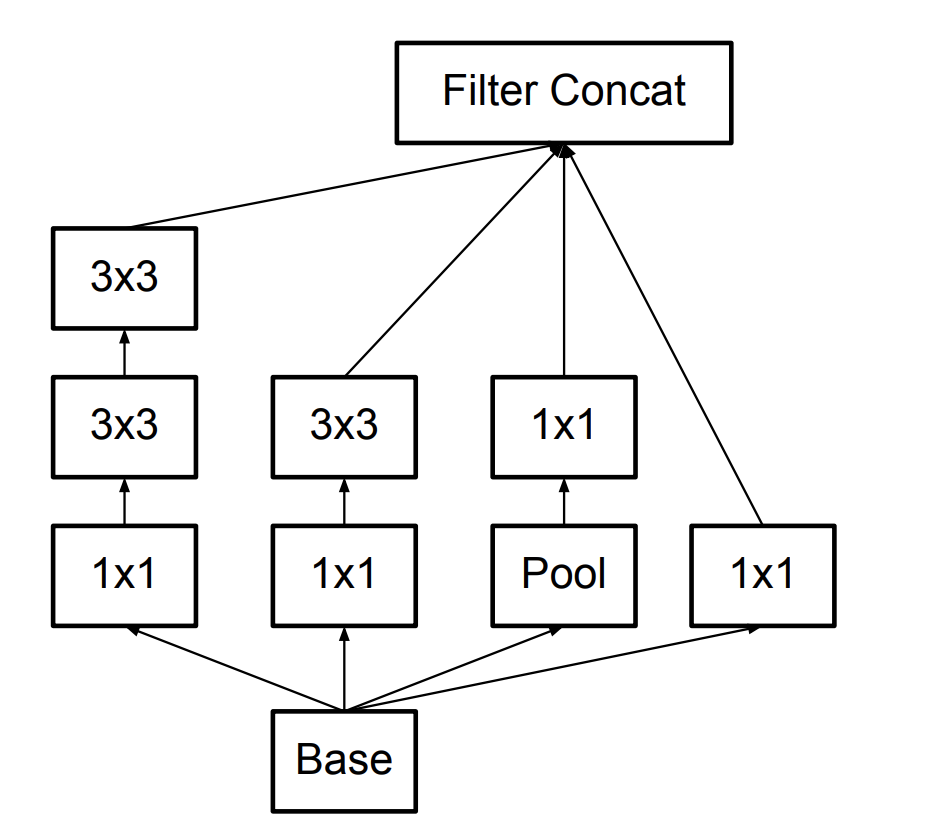
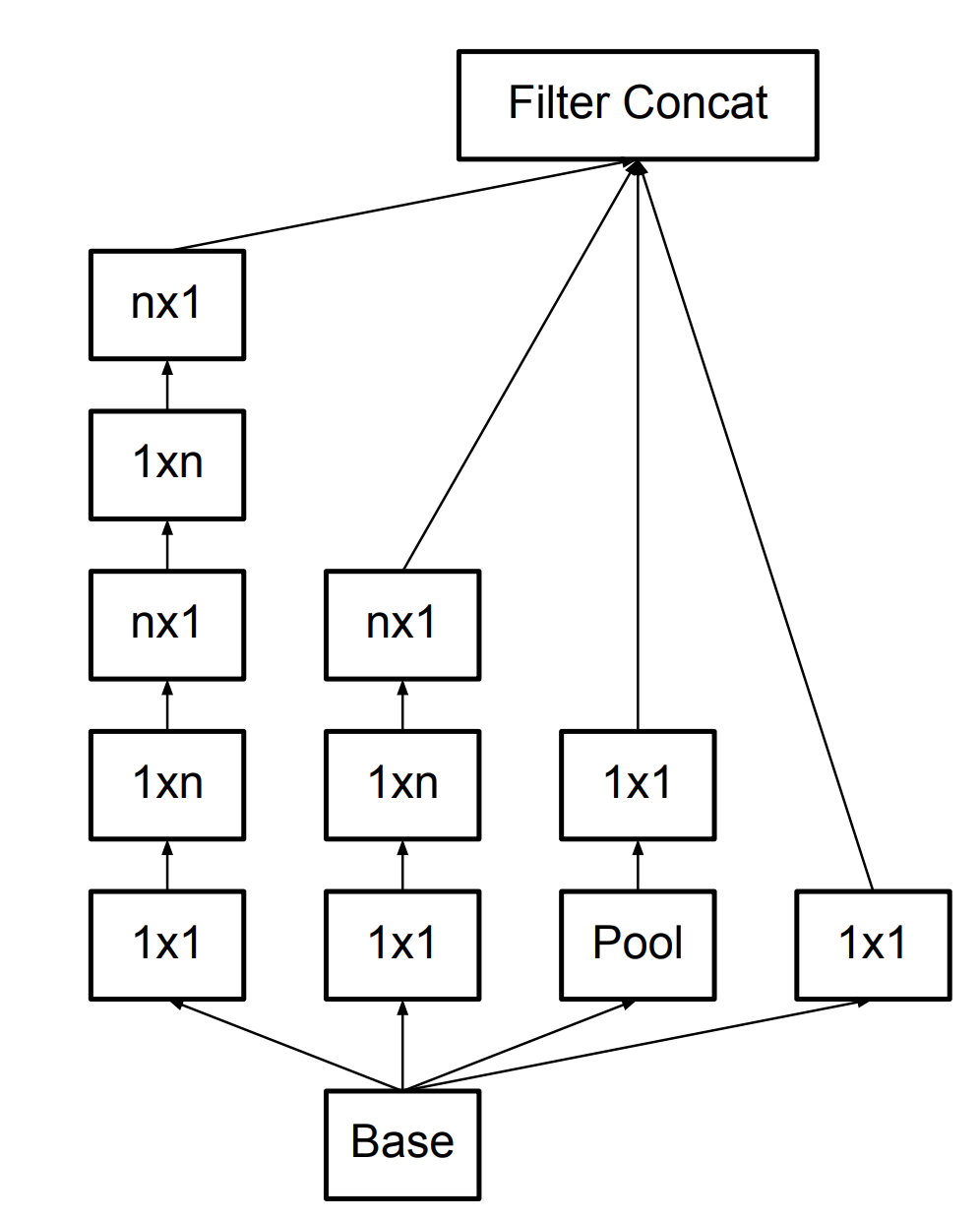
- Spatial Factorization into Asymmetric Convolutions: for example, using a \( 3 \times 1 \) convolution followed by a \( 1 \times 3 \) convolution is equivalent to \( 3 \times 3 \) convolution.
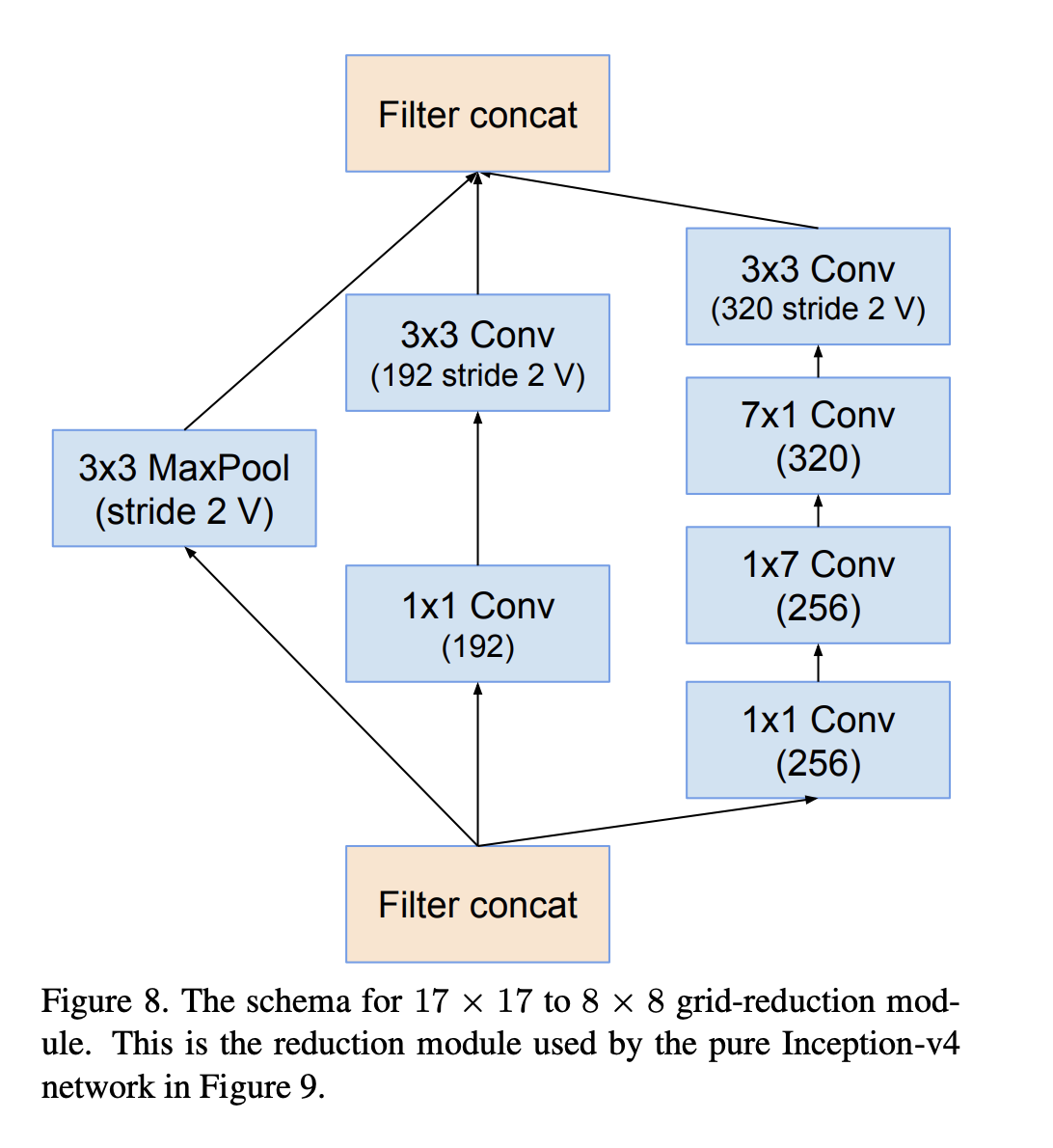
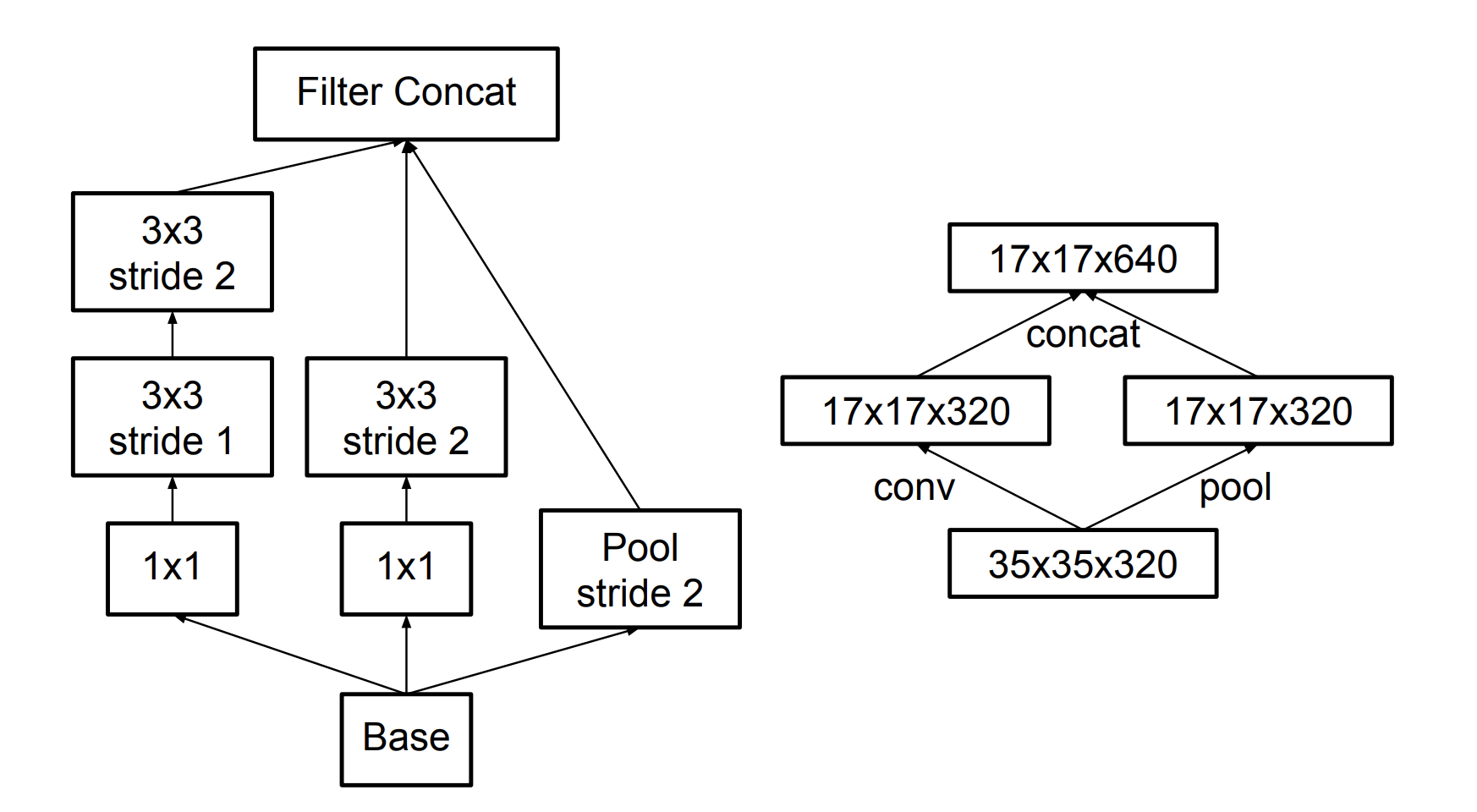
- Efficient Grid Size Reduction: Traditionally, convolutional networks used some pooling operation to decrease the grid size of the feature maps. In order to avoid a representational bottleneck, before applying maximum or average pooling the number of the network filters is expanded. Here a more suitable and efficient method is used to achieve the reduction of feature map size.
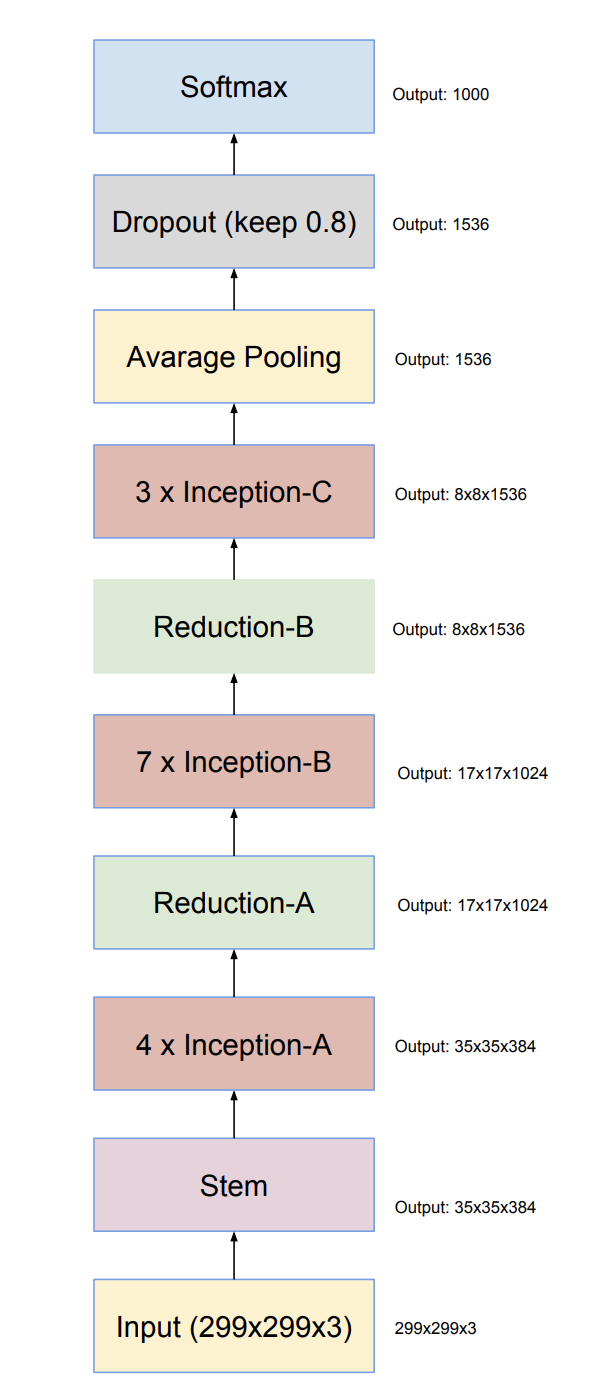
3.Inception-v4 and Inception-ResNet-v2
Inception-v4 applies a further optimization about the stem structure. Inception-ResNet combines Inception architecture with residual connections.
The overall architecture of Inception-v4 is:
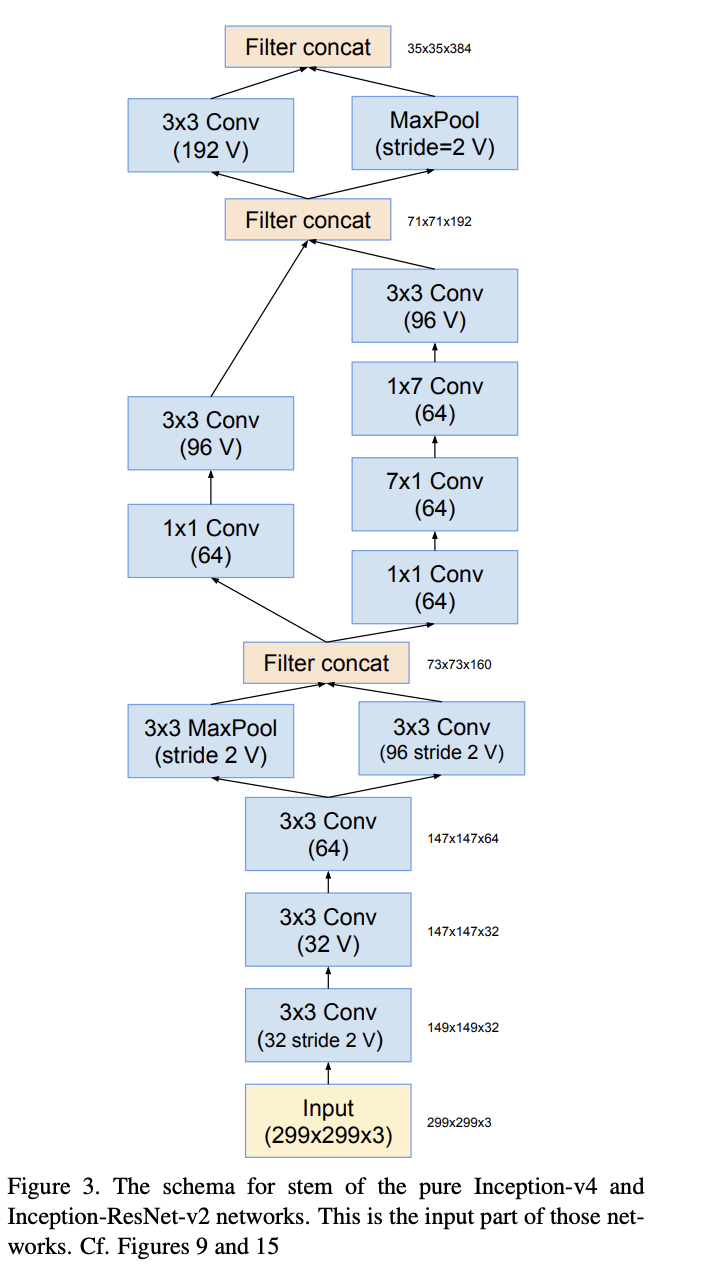
The optimized stem part of Inception-v4:
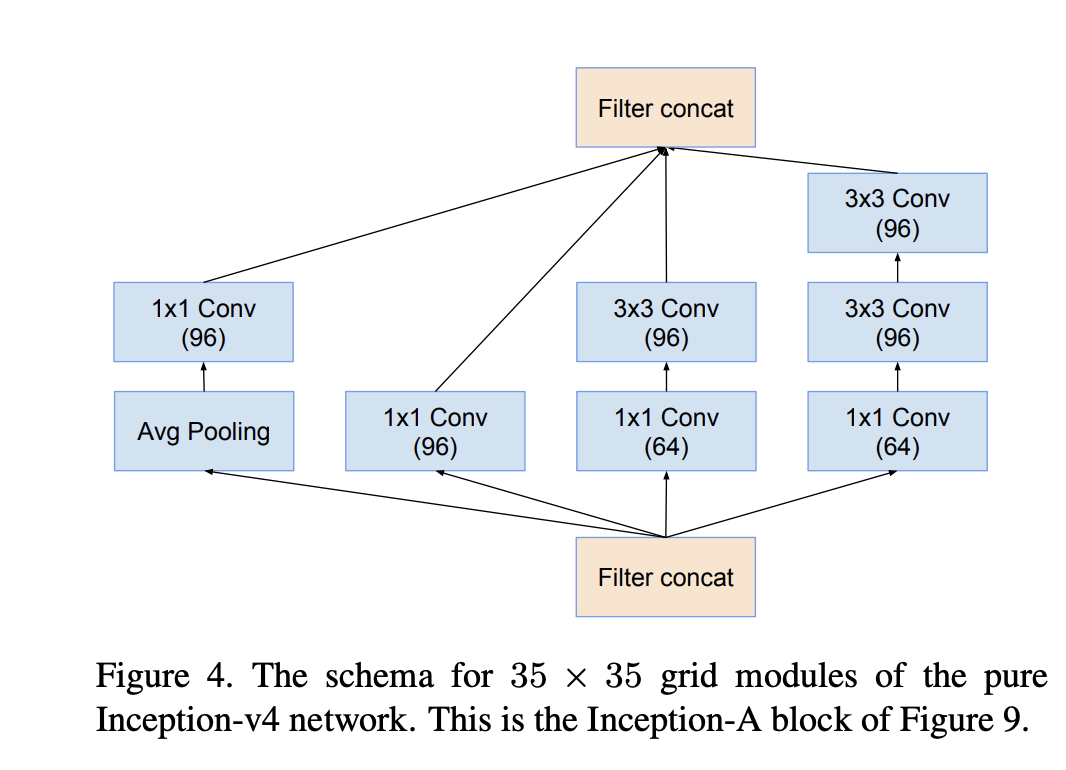
The inception-A block:
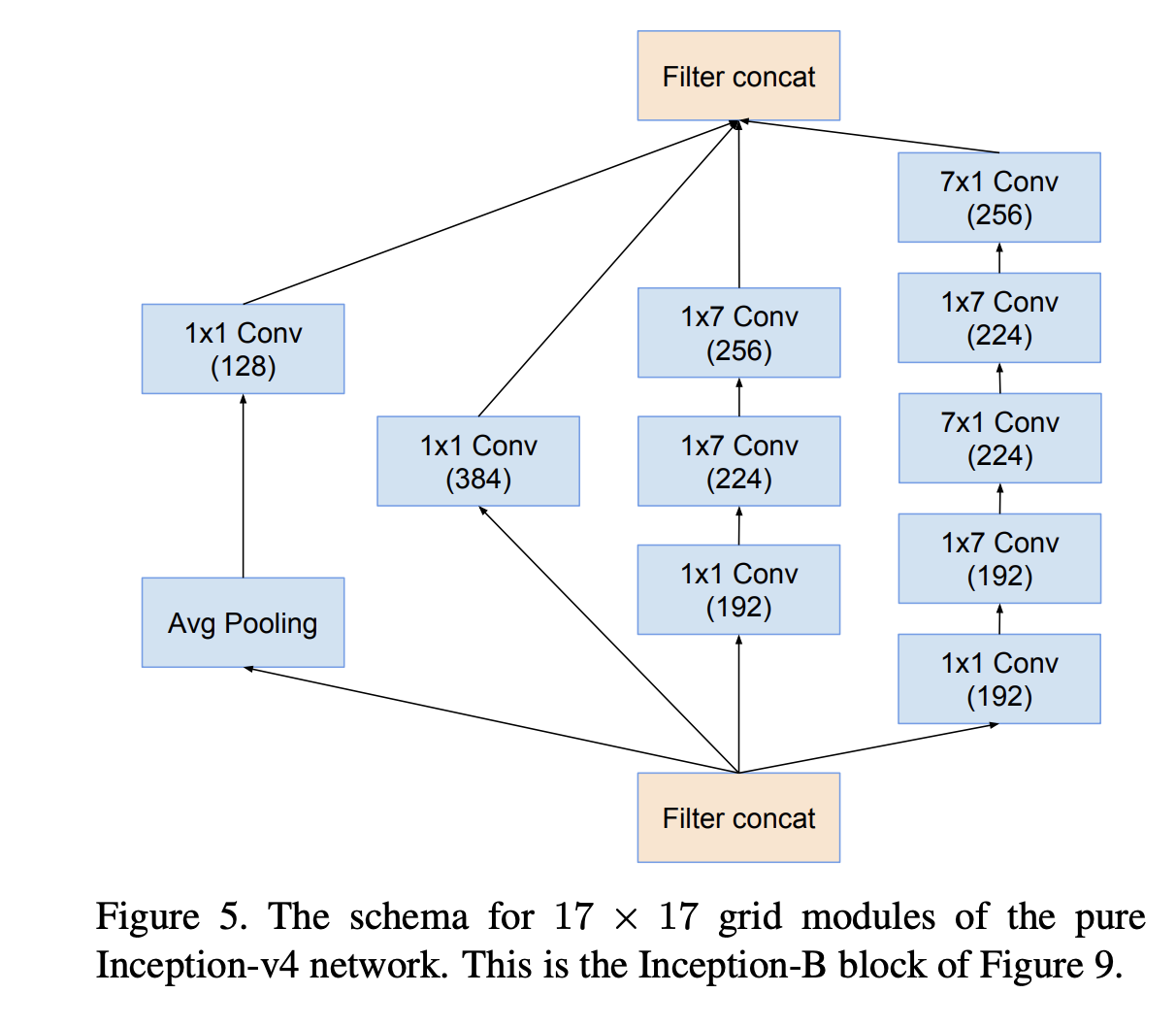
The inception-B block:
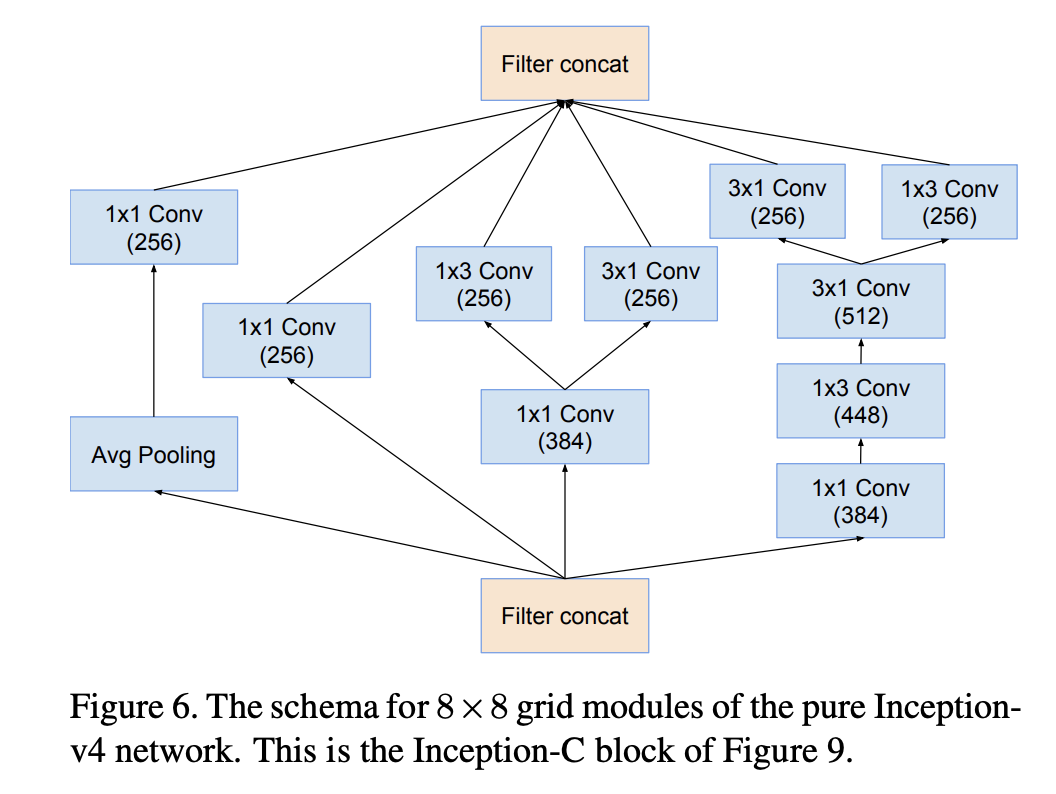
The inception-C block:
The reduction-A block:
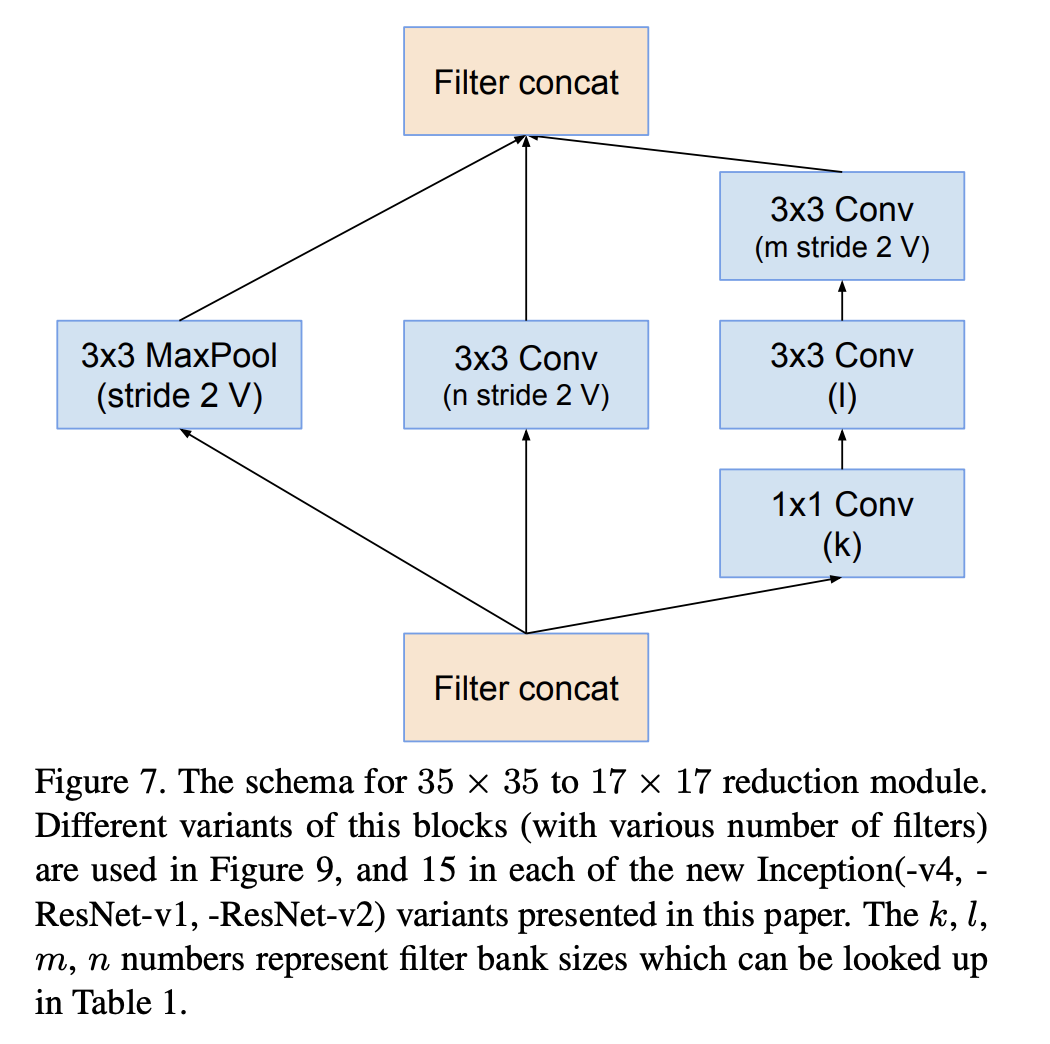
The reduction-B block: