object detection and segmentation
Object detection is a very complex technique that is already widely applied in many fields such as autonomous driving, pedestrian detection, surveillance, gesture estimation and so on. It can be split into multi tasks including object localization, object recognition and classification, object segmentation.
1.two-stage object detection
The detection is composed of two separate steps.
1.1.R-CNN
R-CNN (Recursive Convolutional Neural Network) uses selective search method to extract 2000 candidate regions which is more likey to contain the desired object from the initial image. Then these patches are further processed into the compatible size to overcome the input constraints of some CNN which are used for feature extraction (AlexNet, VGG16, VGG19, ResNet, Inception and so on). Finally these features is feed into one class-specific linear SVM (support vector machine) to get its classification result and bounding box offset.

- selective search method: get region proposals according to the similarity of color, texture
- the labelling of positive and negative samples: the IoU (Intersection over Union) between ground truth bounding box and candidate regions decides if its positive or negative.
- non-maximum suppression (NMS): when there are multiple prediction bounding boxes for the same object and IoU value between them exceeds the threshold, then we keep the prediction bounding box with the maximal prediction probability.
The main disadvantages for R-CNN are:
- the huge computation cost for the selective search method at the initial step.
- Training is a multi-stage pipeline: extracting features, fine-tuning a network with log loss, training SVMs,and finally fitting bounding-box regressors.
- performs a ConvNet forward pass for each object proposal without sharing computation
1.2.Fast R-CNN
To overcome the drawbacks of R-CNN, the Fast R-CNN is proposed.

- the inputs consist of two parts: the entire image and a set of object proposals.
- it still uses the selective search method which is time-consumed.
- The network first processes the whole image with several convolutional and max pooling layers to produce a conv feature map. Then, for each object proposal a region of interest (RoI) pooling layer extracts a fixed-length feature vector from the feature map.
- training is streamlined and single-stage, class and bounding box is trained at the same time using the multi-task loss function.
1.3.Faster R-CNN
It is composed of two modules. The first module is a deep fully convolutional network that proposes regions, and the second module is the Fast R-CNN detector that uses the proposed regions. It replaces the time-consumed selective search method with using the region proposal network (RPN) to get the probable region of interest.
The architecture of Faster R-CNN is demonstrated as follows:

A Region Proposal Network (RPN) takes an image as input and outputs a set of rectangular object proposals, each with an objectness score. We can define some anchor boxes to slide on each point of the feature map. For training RPNs, we assign a binary class label (of being an object or not) to each anchor.
The structure of RPN is depicted as following picture:
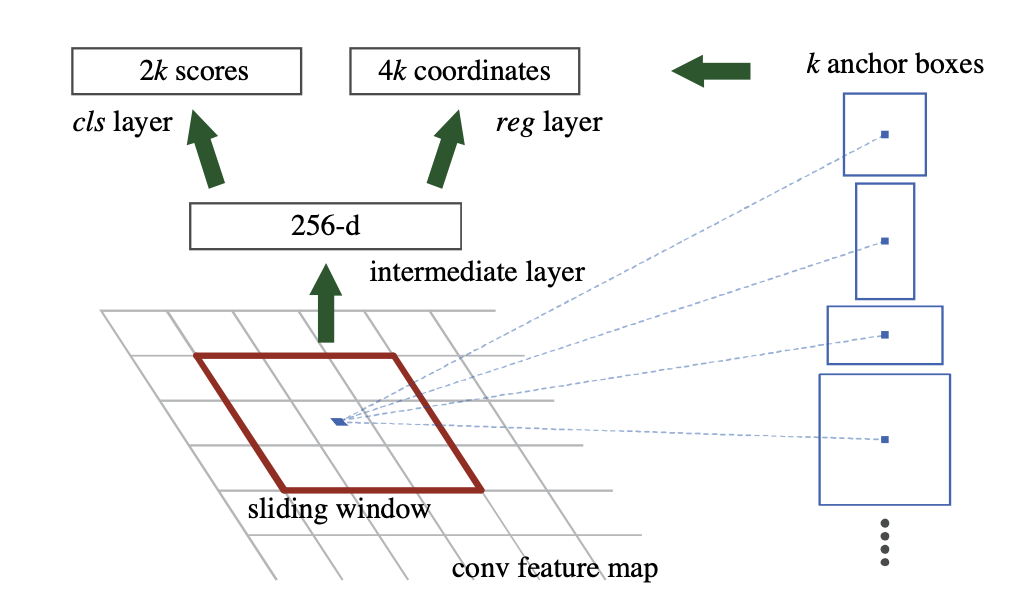
We further merge RPN and Fast R-CNN into a single network by sharing their convolutional features using alternating training.
2.one-stage object detection
There is only one direct steps for detection.
2.1.SSD
Single Short Multibox Detector (SSD) eliminates object proposal generation process instead of a set of default boxes over different aspect ratio and scales per feature map location. SSD generates scores for the presence of each object category in each default box and produces adjustment to the box to better match the object shape. besides, it combines predictions from multi-scale feature maps with different resolution to mutually decide the final prediction result.

During training we need to determine which default boxes correspond to a ground truth detection and train the network accordingly. For each ground truth box we are selecting from default boxes that vary over location, aspect ratio, and scale. We begin by matching each ground truth box to the default box with the best jaccard overlap, we then match default boxes to any ground truth with jaccard overlap higher than a threshold (0.5).
training loss objective is a combination of localization loss and confidence loss. When labelling the training data, most of the default boxes are negatives. This will cause the imbalance between positive and negative training examples. Instead of using all the negative examples, we sort them using the highest confidence loss for each default box and pick the top ones so that the ratio between the negatives and positives is at most \( 3:1\) using hard negative mining method.
2.2.YOLO
You Only Look Once (YOLO) is a simple, lite, end-to-end fast object detector for real-time object detection application.
It splits the input image into an \( S \times S\) grid, If the center of an object falls into a grid cell, that grid cell is responsible for detecting that object. YOLO predicts multiple bounding boxes per grid cell. At training time we only want one bounding box predictor to be responsible for each object.
Each grid cell predicts \( B \) bounding boxes and confidence scores for those boxes. These confidence scores reflect how confident the model is that the box contains an object and also how accurate it thinks the box is that it predicts. Each grid cell also predicts \( C \) conditional class probabilities, These probabilities are conditioned on the grid cell containing an object. we only predict one set of class probabilities per grid cell, regardless of the number of boxes \( B \).
At test time we multiply the conditional class probabili- ties and the individual box confidence predictions.
\[\begin{equation} Pr(Class_i | Object) * Pr(Object) * IOU_{pred}^{truth} = Pr(class_i) * IOU_{pred}^{truth} \end{equation}\]the prediction process is depicted as following picture:
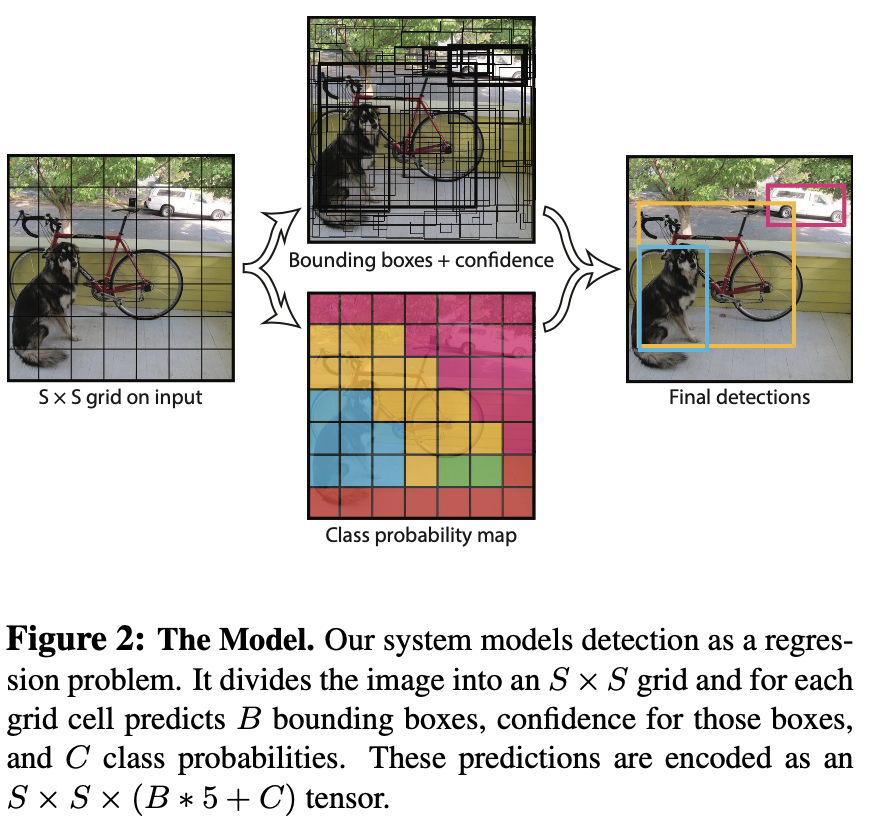
YOLO still lags behind state-of-the-art detection systems in accuracy. While it can quickly identify objects in im- ages it struggles to precisely localize some objects, especially small ones.
3.object segmentation
object instance semantic segmentation is to paint the specific and concrete shape of object after detecting the object.
3.1.Mask R-CNN
Mask R-CNN extends Faster R-CNN by adding a branch for predicting an object mask on each region of interest, in parallel with the existing branch for bounding box regression and label classification. The mask branch is a small FCN applied to each RoI, predicting a segmentation mask in a pixel-to-pixel manner. Mask R-CNN adopts the same two-stage procedure as Faster R-CNN, with an identical first stage (which is RPN). In the second stage, in parallel to predicting the class and box offset, Mask R-CNN also outputs a binary mask for each RoI.
